Medical Simulation
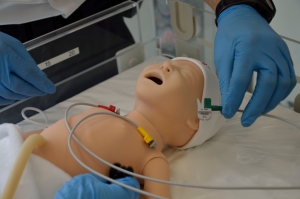
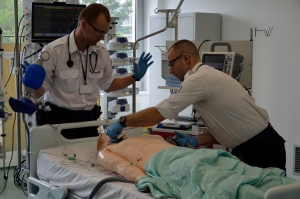
Medical Simulation is a method of teaching that allows students to acquire skills, competencies and knowledge through participation in situations encountered in everyday life.
Role playing and case studies are the most commonly used simulation techniques in teaching. These are methods that allow you to solve problems in the true-to-life conditions and to discuss the case immediately after finishing the exercise. These methods require the teachers to have prior practical experience in the subject.
One of the most important values of simulation is the exploitation of the potential and emotional involvement of teachers and the opportunity to study the case.
Simulation serves following purposes:
- development of complex cognitive skills such as taking appropriate decisions and assessment of situation,
- positive impact on values, students’s beliefs and attitudes,
- understanding the needs of other person,
- improving interpersonal skills,
- eliminating of negative attitudes and behaviours
The advantages of simulation are:
- getting to know student’s own strengths and limitations,
- active participation in the learning process (learners are not passive receivers of information),
- an opportunity to experience the effects of students’ own mistakes,
- immediate feedback for students, reinforcing their commitment.
Simulation is used at all stages of education, in virtually all areas of medicine. In addition to anesthesia and intensive care – pioneer scopes of simulation – it is also needed in surgery, gynecology, cardiology, emergency medicine, neonatology and geriatrics. This form of teaching has been applicable since first years of medical education, starting with first-aid classes and finishing with improving skills of highly experienced doctors.